A novel method of nicotine quantification in electronic cigarette liquids and aerosols†
Abstract
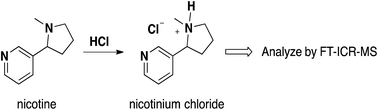
Electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) have emerged as popular electronic nicotine delivery devices (ENDs). However, the general safety and validity of e-cigarettes for nicotine delivery efficacy are still not well understood. This study developed a new method for efficient measurement of nicotine levels in both the liquids (e-liquids) used in e-cigarettes and the aerosols generated from e-cigarettes. Protonation of the pyrrolidine nitrogen of nicotine molecules by addition of excess hydrochloric acid affords an aminium salt that is readily quantified by Fourier transform ion cyclotron mass spectrometry (FT-ICR-MS). The kinetics of nicotine protonation were studied using 1H NMR spectroscopy. Quantitative analyses of nicotine in commercial e-liquids and in the corresponding derived e-cigarette aerosols were carried out using direct infusion FT-ICR-MS. The 1H NMR study of nicotine protonation revealed a first order reaction and an activation energy of 30.05 kJ mol−1. The nicotine levels measured in the commercial e-liquids were within a wide and highly variable range of −2.94% to +25.20% around the manufacturer's stated values. The results indicated considerable differences between the measured levels and the advertised levels of nicotine in the e-liquids. The nicotine quantity measured in aerosols increased linearly both with the nicotine level in e-liquids (same number of puffs) and with the number of puffs (same e-liquids). These data show that quality control of e-liquids and use characteristics are major variables in the efficacy of nicotine delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...