A highly sensitive and label-free electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for beta 2-microglobulin†
Abstract
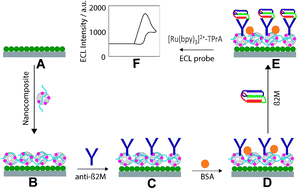
A highly sensitive and label-free electrochemiluminescence (ECL) immunosensor was fabricated for the detection of β-2-microglobulin (β2M) based on a gold nanoparticle-doped@carbon nano-onion chitosan nanocomposite modified cadmium selenide quantum dot screen-printed electrode (QDs-SPE/AuNPs@CNOs-CS) for the first time. The electrode was biocompatible, with increased effective surface area for capturing and binding of a large number of anti-β2M antibodies. Moreover, it afforded high stability, greatly improved the electronic transmission rate and enhanced the capture of photons emitted from the luminophore tris(bipyridine)ruthenium(II) chloride ([Ru(bpy)3]2+Cl), which show great promise for the fabrication of highly sensitive ECL immunosensors. The fabrication process involved immobilization of anti-β2M onto QD-SPE/AuNPs@CNOs-CS pre-blocked by BSA (QDs-SPE/AuNPs@CNOs-CS/anti-β2M/BSA). The principle of ECL detection was based on the increase in the electrostatic attraction between the β2M and [Ru(bpy)3]2+ at a pH above the isoelectric point. The ECL intensity was linearly elevated with the increase in log concentration of β2M from 1 fg mL−1 to 100 ng mL−1 and a detection limit of 1 fg mL−1. The immunosensor demonstrated huge potential to detect β2M in real serum and urine samples for clinical diagnosis. This work showcased QDs-SPE/AuNPs@CNOs-CS as an ideal interface to fabricate a highly sensitive label-free ECL immunosensor to detect other biomarkers of clinical significance.
- This article is part of the themed collection: #RSCPoster Conference


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...