Hollow fiber-based solid–liquid phase microextraction combined with theta capillary electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for sensitive and accurate analysis of methamphetamine†
Abstract
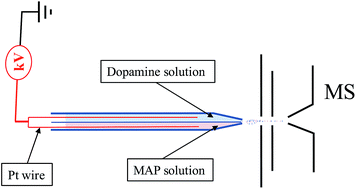
This paper presents a new method for quantitative analysis of methamphetamine (MAP) in urine samples based on hollow fiber-based solid–liquid phase microextraction (HF-SLPME) in combination with theta capillary-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (TC-ESI-MS) detection. In the lumen of the hollow fiber, metal organic frameworks/graphene oxide (MOF/GO) hybrid material dispersed in 1-octanol was used as the acceptor phase for the enrichment of MAP. For TC-ESI-MS detection, the ESI emitter has a theta capillary with two separate channels and one common emitter tip. The MAP solution and the reference dopamine solution were separately loaded into the two channels. The ratio of signal intensities between MAP and dopamine was used for the evaluation of the extraction efficiency. Several experimental parameters influencing the extraction efficiency were investigated and optimized. Under the optimized conditions, the limit of detection was 0.5 ng mL−1, and the linearity range was 2.0–200.0 ng mL−1, with the correlation coefficient (R2) at 0.9997, indicating that the method based on HF-SLPME combined with TC-ESI-MS is sensitive and accurate for the determination of MAP in urine samples and would have utility in other types of trace chemical analyses.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...