Phage displayed anti-idiotypic nanobody mediated immuno-PCR for sensitive and environmentally friendly detection of mycotoxin ochratoxin A
Abstract
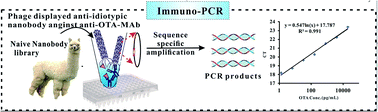
Anti-idiotypic nanobodies (AId-Nbs) are novel antigens that can replace the conventional hapten–protein conjugates of small molecule toxins, serving the same function in the competitive immunoassay. Furthermore, nanobodies show increased sensitivity from naïve (non immunized) phage display libraries because those obtained have a lower affinity than the binding affinity of the target analytes. Here, we demonstrated a new approach for the development of sensitive and environmentally friendly immuno-PCR (IPCR) for OTA based on phage displayed AId-Nbs against anti-OTA monoclonal antibodies. In this study, a phage displayed AId-Nb was selected from a naïve nanobody library. After four cycles of panning, a phage displayed AId-Nb was isolated using a competition-binding biopanning strategy. The half-inhibition concentration (IC50) of the phage-ELISA was 300 pg mL−1, which was 8.83-fold better than that of a conventional ELISA. Furthermore, a non-toxin quantitative IPCR assay was also developed for the detection of ochratoxin A in agri-products based on phage displayed AId-Nbs. The limit of detection (LOD) of the assay is 4.17 pg mL−1, which exhibits a 9-fold improvement over the phage-ELISA. The developed method was successfully validated using OTA contaminated agri-products. Furthermore, novel and environmentally friendly IPCR might have potential applications in a general method for the immunoassay of various toxic small molecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...