Detection of nuclease activity using a simple fluorescence based biosensor†
Abstract
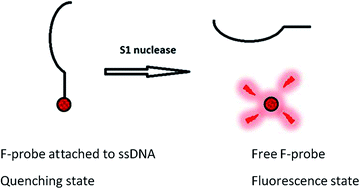
Nucleases are associated with a variety of diseases as they catalyze the degradation of nucleic acids. Their presence as a contaminant could also be a major concern in several molecular biology-related analyses where DNAse and RNAse free environments are required. Here, we report a simple, fluorescence-based biosensor for nuclease detection. The sensor utilizes only one fluorescent molecule attached to a ssDNA molecule building upon a fluorescence-quenching phenomenon taking place between a fluorescent dye and a nucleotide base. The intensity of the fluorescent molecule is quenched by covalently attaching to ssDNA and upon digestion of the ssDNA the fluorescence signal increases dramatically. Consequently, the fluorescence signal can be used to determine the activity of nuclease enzymes for a variety of applications ranging from molecular biology to clinical diagnostics. Compared to available methods, our sensor does not use any additional substances such as cationic polymers, carbon nanotubes or nanoparticles, graphene oxide or silver nanoclusters or a quencher like DABCYL to quench a fluorophore. The simplicity of the detection method makes this an attractive sensor as a low cost, fast and convenient system that can be incorporated into multiple readers for widespread use in virtually all molecular biology-related analyses.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...