In situ preparation of porous Pd nanotubes on a GCE for non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors
Abstract
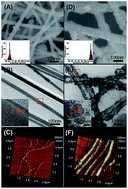
Porous Pd nanotubes were in situ fabricated on a glass-carbon electrode (GCE) via a one-step galvanic replacement reaction by using cheap, flexible, and ultralong copper nanowires as the sacrificial template. The electrode exhibits excellent electrocatalytic performance for non-enzymatic glucose biosensors, thanks to massive pores and high specific surface area. This non-enzymatic glucose biosensor shows a wide linear response range from 5 μM to 10 mM, with a sensitivity of 6.58 μA mM−1 cm−2, and a detection limit of 1 μM (signal-to-noise ratio of 3).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...