1H-NMR metabonomics study of the therapeutic mechanism of total alkaloids and ajmalicine from Rauvolfia verticillata in spontaneously hypertensive rats†
Abstract
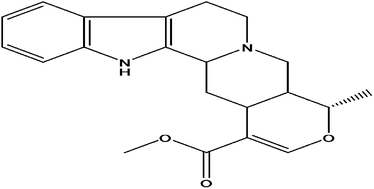
The total alkaloids extracted from Rauvolfia verticillata have been developed into drugs-Verticil to treat hypertension. It has a slow and sustained reduction in blood pressure, for the treatment of early and mild hypertension. Ajmalicine, an indole alkaloid from total alkaloids, has been shown to not only reduce blood pressure but also expand blood vessels. However, the mechanism of the antihypertensive effect of total alkaloids and ajmalicine has not been fully characterized. In this research, we chose to study a hypertensive rodent model, spontaneously hypertensive rats. Spontaneously hypertensive rats are a useful model for the study of essential hypertension which is a complex, polygenic, and multifactorial disorder. Studies suggest the usefulness of an 1H-NMR-based metabonomic approach using spontaneously hypertensive rats for the study of hypertension. The spontaneously hypertensive rats were given total alkaloids and ajmalicine by oral gavage from 10 to 16 weeks of age. Plasma samples were analyzed using 1H-NMR spectroscopy and metabolic information was extracted from the NMR data by principal components analysis as well as partial least square-discrimination analysis in order to develop biomarkers associated with hypertension. The metabolic pathways of small molecule metabolites in plasma were investigated to explain the content changes. The results obtained showed that ajmalicine only has a weak effect for hypertension. Total alkaloids exert their antihypertensive effect by reducing the level of tyrosine and increasing the level of choline and leucine. The use of total alkaloids plus ajmalicine showed its antihypertensive effect more strongly than total alkaloids.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...