Determining striatal extracellular glutamate levels in xCT mutant mice using LFPS CE-LIF
Abstract
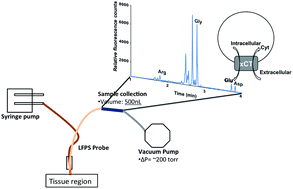
Glutamate analysis is useful for the study of many neurochemical processes. In vivo sampling techniques and sample assays provide a platform for monitoring extracellular glutamate levels in the central nervous system of animal models. Low flow push–pull perfusion sampling is used here to sample from the mouse striatum to understand basal extracellular glutamate levels. The 500 nL perfusate samples are pH adjusted with minimal dilution of 1.2 fold prior to derivatization for glutamate measurements. The method optimized for glutamate labelling and measurement involves the use of capillaries for addition of 100 nL solutions to samples. Quantitation of glutamate in the derivatized samples was accomplished with capillary electrophoresis-laser induced fluorescence. Glutamate and aspartate levels were monitored in C3H/HeSnJ controls and C3H/HeSnJ-Slc7a11sut mutants to understand cystine-glutamate transporter (xCT) function. The study of basal glutamate levels used 4 groups: males and females of both control and mutant mice (each N = 5). Using this approach, extracellular glutamate levels in mouse striatum were found to range between 2.68(±0.51) μM and 1.84(±0.40) μM. As expected, extracellular glutamate was lower in the striatum of sut mutant males. Control females, however, showed lower glutamate overall and no difference between genotypes. Overall, a method of LFPS collection and CE-LIF quantitation shows promise for study of glutamate in this model system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...