Discontinuous double mechanism for the retention of some cation-type oximes on a hydrophilic stationary phase in liquid chromatography
Abstract
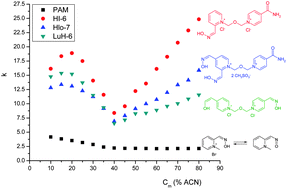
Retention data (retention factor versusacetonitrile content in the mobile phase) on a zwitterionic hydrophilic

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...