Anti-Aβ drug candidates in clinical trials and plasmonic nanoparticle-based drug-screen for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
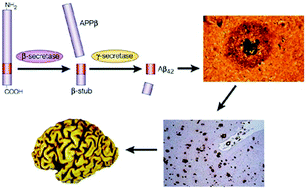
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common cause of neurodegenerative disorder in elderly people, and has become a social problem in aging societies globally. Amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregates (i.e., Aβ fibrils and plaques) present in the brains of AD patients are hallmarks of AD. Although various promising anti-Aβ drugs have been tested in pre-clinical and randomized controlled trials, the trial results have not yet been translated into clinical practice due to increasing time and cost of drug development. Recent investigations have addressed how the formation of Aβ aggregates is influenced by the surface of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) to obtain a detailed understanding of the in vivo process of amyloid formation. Particularly, AuNPs catalytically provide nucleation sites to accelerate the formation of Aβ aggregates. Moreover, AuNPs have great potential as a sensing tool due to their optical property. Employing this dual function (i.e., catalytic and optical property), AuNP-based colorimetry is highlighted as a simple and innovative method for monitoring the efficacy of anti-Aβ reagents. In this review, we briefly survey important developments and designs of anti-Aβ drugs. The significance and perspectives of AuNP-based drug-screening in pharmacologic research are also discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...