Resonance Raman detection of antioxidants using an iron oxide nanoparticle catalysed decolourisation assay
Abstract
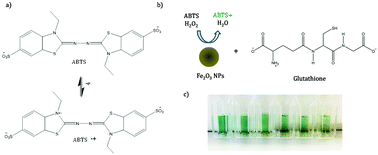
Nanozymes are metal nanoparticles with catalytic properties that can be used to oxidise peroxidase substrates giving a colorimetric response which can be detected using UV-vis, and recently, Raman spectroscopy. Due to their ease of synthesis and increased stability, nanozymes are being increasing investigated to replace conventional enzymes for the detection of biomolecules. Here we exploit the catalytic activity of iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles combined with the substrate 2,2-azinobis(3-ethyl-benzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) in a decolourisation assay for the detection of antioxidants. Fe2O3 nanoparticles were used to catalyse the oxidation of ABTS to its green radical cation which, upon the addition of an antioxidant, resulted in a decolourisation due to the reduction of the radical cation caused by the hydrogen donating antioxidant. The assay was applied for the detection of multiple antioxidants (glutathione, chlorogenic acid and ascorbic acid), and was followed by monitoring the resonance Raman scattering from the ABTS solution using a portable Raman system with 785 nm laser excitation. This novel assay has the potential to be optimised to detect antioxidant activity in body fluid with low limits of detection with point of use monitoring.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...