A convenient approach to facilitate monitoring Gaucher disease progression and therapeutic response
Abstract
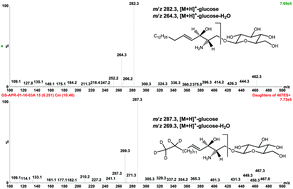
Gaucher disease (GD) is caused by mutations on the GBA1 gene leading to deficiency in acid β-glucosidase (GCase) and subsequent accumulation of its substrates, glucosylceramide (GlcC) and glucosylsphingosine (GlcS). GlcS in plasma has been proposed as a highly sensitive and specific biomarker for the diagnosis of GD and for monitoring disease progression and response to therapy. Here we report a novel robust and accurate hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometric method (HILIC-MS/MS) for the direct measurement of glucosylsphingosine (GlcS) in dried plasma spots (DPS). The method was also capable of resolving the isomeric pair, glucosylsphingosine and galactosylsphingosine, the latter of which was proposed as a promising biomarker for Krabbe disease. The method was fully validated and applied to the analysis of 19 GD patients and carriers. The GlcS levels in 9 GD type I patients who have been on enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) were reduced to a mean of 31.0 nM, much lower compared to a pre-treated specimen at a level of 85.8 nM, but still significantly elevated compared to healthy controls. GlcS concentrations in three treated type III GD patients were much lower compared to an untreated patient. In our preclinical GD studies, 4L;C* mice (subacute nGD model) exhibited comparable levels of plasma GlcS, but had much higher GlcS accumulation in the brain than those of 9V/null mice (chronic neuropathic GD model). Our method for the measurement of GlcS in DPS proved to be a very convenient approach for sample collection, storage and shipping nationwide and internationally.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...