A novel two-photon fluorescent probe with a long Stokes shift and a high signal-to-background ratio for human NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (hNQO1) detection and imaging in living cells and tissues†
Abstract
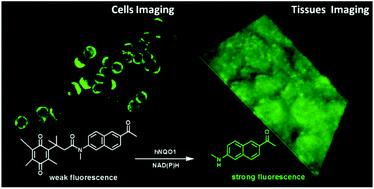
In recent years, many activatable fluorescent probes have been developed for hNQO1 detection. However, most of the reported fluorescent probes are susceptible to the interferences of endogenous fluorescence and have the drawback of inadequate penetration depth. Very recently, researchers have reported a two-photon excitation (TPE) fluorescent probe for hNQO1 detection. Nevertheless, this probe only exhibits a compromised signal-to-background ratio, and has not been applied to image hNQO1 in living tissues. Herein, a novel TPE fluorescent probe, trimethyl locked quinone caged Acedan (Q3CA-P), has been developed for hNQO1 detection and imaging in living cells and tissues. Q3CA-P displays over 25-fold enhancement in fluorescence intensity toward hNQO1 with a Stokes shift over 100 nm in one-photon excitation and exhibits a very low detection limit of 5.6 ng mL−1. The imaging experiments performed in tumour cells and tissue slices using Q3CA-P demonstrate that Q3CA-P could image the endogenous hNQO1 with high selectivity and sensitivity with a TPE probing depth of 120 μm. Thus, our probe may have great potential for use in cancer diagnosis and image-guided surgery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...