ProxyPhos sensors for the detection of negatively charged membranes†
Abstract
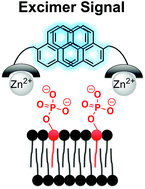
Membrane-embedded negatively charged phospholipids (MENCP) can be used as biomarkers for a range of biological processes, including early detection of apoptosis in animal cells, drug-induced phospholipidosis, and selective detection of bacterial over animal cells. Currently, several technologies for the detection of apoptosis and bacterial cells are based on the recognition of MENCPs, including the AnnexinV stain and PSVue™ probes. As probes, these technologies have limitations, the most significant of which is the need for washing the unbound probe away to achieve optimal signal. In contrast, a turn-on chemosensor selective for MENCP would address this shortcoming, and allow for a more rapid protocol for the detection of apoptosis, bacteria and for other relevant applications. In this work, the aim was to explore whether ProxyPhos chemosensors, previously reported by our group for the detection of proximally phosphorylated peptides and proteins, could be re-purposed for the detection of MENCPs. Six lead ProxyPhos sensors were screened against synthetic vesicles containing biologically relevant negatively charged phospholipids including phosphatidic acid (PA), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), cardiolipin (CL) and phosphatidylserine (PS). Through these screens, ProxyPhos sensors exhibiting high selectivity for the detection of MENCPs over zwitterionic lipids were identified. Particular selectivity was observed for PA and CL. Sensitivity of the lead sensors for MENCPs was suitable for the detection of apoptosis: ProxyPhos detected vesicles containing as little as 2.5% PS and detected camptothecin-induced apoptosis in mammalian cells in flow cytometry experiments. The results suggest that ProxyPhos sensors can be used for the detection of MENCPs in synthetic vesicles and live mammalian cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...