Sedimentation coefficient distributions of large particles
Abstract
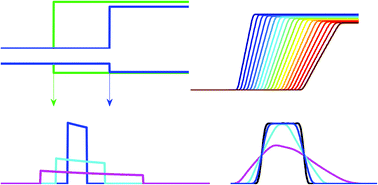
The spatial and temporal evolution of concentration boundaries in sedimentation velocity analytical ultracentrifugation reports on the size distribution of particles with high hydrodynamic resolution. For large particles such as large protein complexes, fibrils, viral particles, or nanoparticles, sedimentation conditions usually allow migration from diffusion to be neglected relative to sedimentation. In this case, the shape of the sedimentation boundaries of polydisperse mixtures relates directly to the underlying size-distributions. Integral and derivative methods for calculating sedimentation coefficient distributions g*(s) of large particles from experimental boundary profiles have been developed previously, and are recapitulated here in a common theoretical framework. This leads to a previously unrecognized relationship between g*(s) and the time-derivative of concentration profiles. Of closed analytical form, it is analogous to the well-known Bridgman relationship for the radial derivative. It provides a quantitative description of the effect of substituting the time-derivative by scan differences with finite time intervals, which appears as a skewed box average of the true distribution. This helps to theoretically clarify the differences between results from time-derivative method and the approach of directly fitting the integral definition of g*(s) to the entirety of experimental boundary data.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...