Acoustic monitoring of changes in well-defined hyaluronan layers exposed to chondrocytes†
Abstract
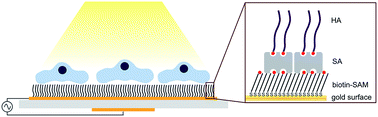
The interaction of human-derived chondrocytes and thin hyaluronan layers was studied using the quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D) technique combined with light microscopy. This approach allowed unique real-time monitoring of the interface between the cells and the sensor surface. Our results suggest that the hyaluronan layer is rapidly degraded by chondrocytes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...