Spatial organization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms probed by combined matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry and confocal Raman microscopy†
Abstract
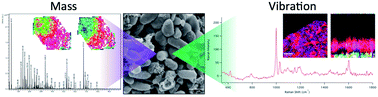
Bacteria growing as surface attached biofilms differ significantly from planktonic cells in several important traits that are reflected in the spatiotemporal organization of the cells and the extracellular polymeric substances they secrete. The structural and chemical features that define these biofilms are explored here using a combination of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI MS) and confocal Raman microspectroscopies (CRM) to characterize and compare the composition and distribution of biomolecules found in biofilms and planktonic cells of the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Three-day old P. aeruginosa biofilms show dramatic differences in molecular composition compared to planktonic cultures. CRM reveals that wild-type planktonic cell Raman spectra are characterized by bands linked to cellular constituents and are dominated by contributions from DNA- and RNA-related bands. In contrast, biofilm spectra are dominated by bands characteristic of glycolipids – rhamnolipids – polysaccharides and by secreted proteins. LDI MS was applied in turn to identify the rhamnolipids present in the biofilm. Experiments were also conducted using an acyl homoserine lactone quorum sensing-deficient mutant (ΔlasIΔrhlI), which is incapable of producing rhamnolipids. CRM and LDI MS analyses revealed that while molecular composition of the planktonic quorum sensing-deficient cells is similar to that of the wild-type planktonic cells, several compositional differences are observed in the mutant after biofilm growth, including complete absence of detectable rhamnolipids. CRM vibrational spectra of the mutant cells are very similar for planktonic and biofilm growth conditions, indicating that biofilm formation is greatly hindered in the absence of functioning quorum sensing machinery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...