Association rule mining of cellular responses induced by metal and metal oxide nanoparticles†
Abstract
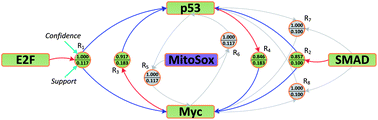
Relationships among fourteen different biological responses (including ten signaling pathway activities and four cytotoxicity effects) of murine macrophage (RAW264.7) and bronchial epithelial (BEAS-2B) cells exposed to six metal and metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs) were analyzed using both statistical and data mining approaches. Both the pathway activities and cytotoxicity effects were assessed using high-throughput screening (HTS) over an exposure period of up to 24 h and concentration range of 0.39–200 mg L−1. HTS data were processed by outlier removal, normalization, and hit-identification (for significantly regulated cellular responses) to arrive at reliable multiparametric bioactivity profiles for the NPs. Association rule mining was then applied to the bioactivity profiles followed by a pruning process to remove redundant rules. The non-redundant association rules indicated that “significant regulation” of one or more cellular responses implies regulation of other (associated) cellular response types. Pairwise correlation analysis (via Pearson's χ2 test) and self-organizing map clustering of the different cellular response types indicated consistency with the identified non-redundant association rules. Furthermore, in order to explore the potential use of association rules as a tool for data-driven hypothesis generation, specific pathway activity experiments were carried out for ZnO NPs. The experimental results confirmed the association rule identified for the p53 pathway and mitochondrial superoxide levels (via MitoSox reagent) and further revealed that blocking of the transcriptional activity of p53 lowered the MitoSox signal. The present approach of using association rule mining for data-driven hypothesis generation has important implications for streamlining multi-parameter HTS assays, improving the understanding of NP toxicity mechanisms, and selection of endpoints for the development of nanomaterial structure–activity relationships.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analytical Toxicology of Nanoparticles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...