Electrochemical piezoelectric-excited millimeter-sized cantilever (ePEMC) for simultaneous dual transduction biosensing†
Abstract
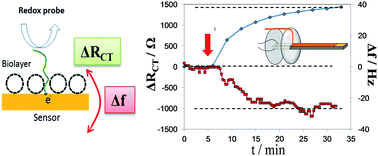
A dual mode electrochemical piezoelectric-excited millimeter cantilever (ePEMC) sensor is reported for simultaneous in-liquid biochemical sensing. The ePEMC incorporates mass-sensing measurement of dynamic-mode cantilevers with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) commonly employed for transduction in sensitive electrochemical biosensors. Such an integrated design allows for simultaneous and continuous measurement of resonant frequency shift (Δf) and charge transfer resistance (RCT) as a target analyte binds to the sensor gold surface (0.5 mm2) via electromechanical and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, respectively. The properties of ePEMC are demonstrated in three experiments: (1) resonant frequency response to electrochemically-deposited metal thin-films, (2) resonant frequency response to adsorption of thiolated ssDNA and model proteins with subsequent EIS sensing, and (3) simultaneous resonant frequency and charge transfer resistance response to model chemisorption of a short-chain thiol molecule, mercaptohexanol. Adsorption of all model binding analytes caused decrease in sensor resonant frequency and increase in charge transfer resistance. Comparison of sensor response to binding of protein and thiol molecules showed the two simultaneously transduced signals were proportional and showed the same kinetics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...