Fluorescence assay for glycan expression on living cancer cells based on competitive strategy coupled with dual-functionalized nanobiocomposites
Abstract
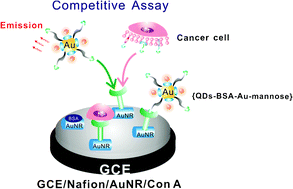
Cell surface glycans are a class of sophisticated biomolecules related to cancer development and progression, and their analysis is of great significance for early cancer diagnosis and treatment. In this paper, we proposed a fluorescence assay to evaluate glycan expression on living cancer cells based on a competitive strategy coupled with dual-functionalized nanobiocomposites. The competitive assay was conducted between living cancer cells and thiomannosyl derivatives using concanavalin A (Con A)-modified electrode as the interaction platform. To impart fluorescence signaling ability to competitive derivatives, quantum dots (QDs) were anchored on BSA-protected Au nanoparticles, and thiomannosyl derivatives were further immobilized on the nanoparticle surface through Au–S binding. Due to the spacing between QDs and Au nanoparticles by BSA, the {QDs–Au–BSA–mannose} nanobiocomposites maintained the fluorescence of QDs and showed binding ability with the Con A-modified electrode. Au nanorods (AuNRs)-modified electrode was used as an effective substrate to immobilize Con A. This assay was successfully applied to the analysis of two cancer cells lines (A549 and QGY-7701). The method is simple and shows promise for the study of glycan expression on living cancer cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...