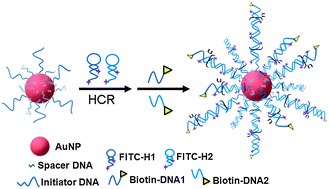
A DNA nanopolylinker was designed as a three dimensional nanoprobe with high loading of signal molecules for amplifying the biosensing signal. The nanoprobe was prepared by hybridization chain reaction engineering dsDNA polymerization on initiator DNA modified Au nanoparticle with two kinds of small molecule, for example, FITC-labeled DNA hairpins. The core–shell conjugate that was formed contained approximately 320 FITC molecules for further binding of signal molecules. With a sandwich-type immunoreaction and a biotin-streptavidin affinity reaction, the biotinylated core–shell nanoprobe was immobilized on the immunosensor surface, and the FITC molecules then bound enzyme labeled anti-FITC antibody to catalyze a silver deposition process, leading to a novel cascade signal amplification strategy. By combining the proposed strategy with stripping analysis of the deposited silver, an ultrasensitive immunoassay method for biomarker detection was developed. Under optimal conditions, this method showed a linear detection range over 5 orders of magnitude for carcinoembryonic antigen with a detection limit of 1.2 fg mL−1 (about 18 molecules in 5.0 μL sample). The preparation of DNA nanopolylinker was simple and economic, and it could be used as a universal and multifarious probe for different bioanalytical techniques and showed the promising potential of the signal amplification strategy in the future design of biosensing methodology.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...