Structural characterization of synthetic polymers using thermal-assisted atmospheric pressure glow discharge mass spectrometry†
Abstract
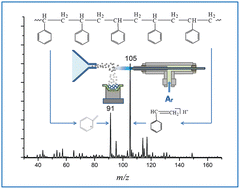
With the development of material science and the practical needs of the polymer industry, rapid characterization of synthetic polymers using mass spectrometry is of sustainable interest. Herein a new method for characterizing synthetic polymers using thermal-assisted atmospheric pressure glow discharge mass spectrometry (TA-APGD-MS) is established. After illustration of the mechanism of ion formation, typical polymer samples such as polystyrene (PS), polyoxymethylene (POM) and poly (butanediol succinate) (PBS) were directly characterized at the molecular level using TA-APGD-MS. The thermal degradation products of synthetic polymers including monomer units and/or other fragments were rapidly detected by tandem mass spectrometry, providing rich information about the chemical composition for the structural characterization of homo- and co-polymers. The result suggests that TA-APGD-MS allows direct and rapid analysis of both synthetic homo-polymers and co-polymers under ambient conditions without any sample pretreatment. This method features high throughput, high sensitivity and rich information, showing promising applications in polymer science.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...