Assessing the responses of cellular proteins induced by hyaluronic acid-modified surfaces utilizing a mass spectrometry-based profiling system: Over-expression of CD36, CD44, CDK9, and PP2A†
Abstract
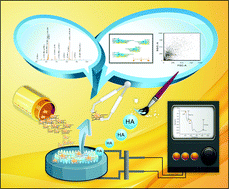
The cell responses to
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of Chemical and Materials Engineering, National Yunlin University of Science and Technology, 123 University Road, Section 3, Douliou, Yunlin, 64002 Taiwan, R.O.C
E-mail:
twchung@yuntech.edu.tw
Tel: +886-5-5342601
b
Department of Medical Imaging and Radiological Sciences, Kaohsiung Medical University, 100, Shi-Chuan 1st Road, Kaohsiung 807, Taiwan, R.O.C
E-mail:
yctyan@kmu.edu.tw
Tel: +886-7-3121101 ext. 2357
c Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
d Department of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
e National Sun Yat-Sen University-Kaohsiung Medical University Joint Research Center, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
f Center of Excellence for Environmental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
g College of Pharmacy, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C.
The cell responses to

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
M. Yang, S. Jong, C. Lu, Y. Lin, P. Chiang, Y. Tyan and T. Chung, Analyst, 2012, 137, 4921 DOI: 10.1039/C2AN35368G
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
