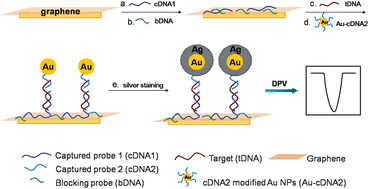
Sensitive and selective detection of DNA is in urgent need due to its important role in human bodies. Many disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease and various cancers, are closely related with DNA damage. In this work, a novel electrochemical DNA biosensor was constructed on a DNA-assembling graphene platform which provided a robust, simple and biocompatible platform with large surface area for DNA immobilization. The as-designed DNA sensor was fabricated by directly assembling captured ssDNA on a graphene-modified electrode through the π–π stacking interaction between graphene and ssDNA bases. Then, the target DNA sequence and oligonucleotide probes-labeled AuNPs were able to hybridize in a sandwich assay format, following the AuNPs-catalyzed silver deposition. The deposited silver was further detected by differential pulse voltammetry. Owing to the high DNA loading ability of graphene and the distinct signal amplification by AuNPs-catalyzed silver staining, the resulting biosensor exhibited a good analytical performance with a wide detection linear range from 200 pM to 500 nM, and a low detection limit of 72 pM. Additionally, the biosensor was proved to be able to discriminate the complementary sequence from the single-base mismatch sequence. The simple biosensor is promising in developing electronic, on-chip assays in clinical diagnosis, environmental control, and drug discovery.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...