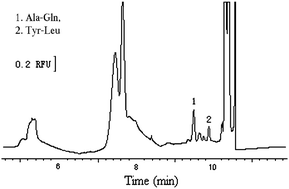
In this paper, we developed a simple and effective on-line focusing technique combining dynamic pH junction and sweeping by capillary electrophoresis (CE) with laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) detection. Dynamic pH junction–sweeping is defined when the sample has a different buffer pH (dynamic pH junction condition) and is devoid of micelles (sweeping condition) relative to the background electrolyte (BGE). This hyphenated focusing mode was applied to the sensitive and selective focusing of four dipeptides: Tyr–Phe, Tyr–Leu, Trp–Gly, and Ala–Gln. Picomolar detectability of these dipeptides by CE–LIF detection was demonstrated through effective focusing of large sample volumes (up to 39% capillary length) using the dual pH junction-sweeping focusing mode. 25 mmol L−1sodium dihydrogen phosphate, pH 2.5 was used as the sample matrix, and 100 mmol L−1borate, 21 mmol L−1sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS), 16 mmol L−1 Brij35, pH 9.0 as the background solution (BGS). The concentration detection limits (S/N = 3) of the four dipeptides were in the range of 1.0–5.0 pmol L−1. The developed method has been successfully used for the determination of dipeptides in human serum samples.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...