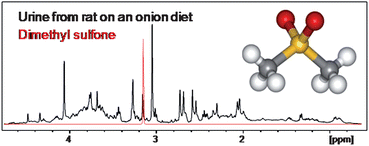
An exploratory NMR nutri-metabonomic investigation reveals dimethyl sulfone as a dietary biomarker for onion intake
Abstract
The metabolome following intake of onion by-products is evaluated. Thirty-two rats were fed a diet containing an onion by-product or one of the two derived onion by-product fractions: an

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...