Correction of axial chromatic aberrations in confocal Raman microspectroscopic measurements of a single microbial spore†
Abstract
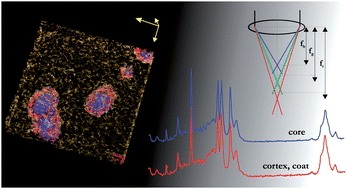
Herein we describe a strategy for correcting the longitudinal or axial component of chromatic aberration in
- This article is part of the themed collection: Optical Diagnosis

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...