PAMAM dendrimer-enhanced DNA biosensors based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
Abstract
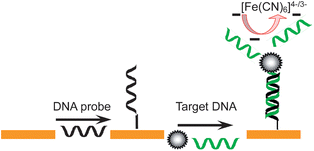
A novel, simple and sensitive DNA biosensor based on DNA–poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimer nanoconjugates was developed by using the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...