Continuous monitoring of ascorbate transport through neuroblastoma cells with a ruthenium oxide hexacyanoferrate modified microelectrode
Abstract
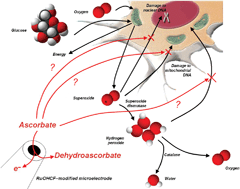
The uptake of ascorbate by neuroblastoma cells using a ruthenium oxide hexacyanoferrate (RuOHCF)-modified carbon fiber disc (CFD) microelectrode (r = 14.5 μm) was investigated. By use of the proposed electrochemical sensor the amperometric determination of ascorbate was performed at 0.0 V in minimum essential medium (MEM, pH = 7.2) with a limit of detection of 25 μmol L−1. Under the optimum experimental conditions, no interference from MEM constituents and reduced glutathione (used to prevent the oxidation of ascorbate during the experiments) was noticed. The stability of the RuOHCF-modified electrode response was studied by measuring the sensitivity over an extended period of time (120 h), a decrease of around 10% being noticed at the end of the experiment. The rate of ascorbate uptake by control human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells, and cells transfected with wild-type Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase (SOD WT) or with a mutant typical of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (SOD G93A), was in agreement with the level of oxidative stress in these cells. The usefulness of the RuOHCF-modified microelectrode for in vivo monitoring of ascorbate inside neuroblastoma cells was also demonstrated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...