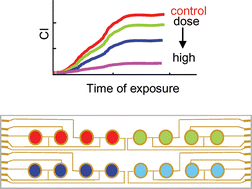
We report a new technique for the continuous and real-time measurement of microparticle-induced cellular responses using a real-time cell-electronic sensing (RT-CES) technology. The method involves the use of microelectrode-embedded microwells seeded with one of two lung cancer carcinoma cell lines (A549 and SK-MES-1), allowing for continuous measurements of impedance. The change in impedance that is automatically converted to the cell index is linearly correlated with the numbers of the seeding cells during the log phase, providing quantitative measurement of cytotoxicity. After 24 h of initial incubation in 96 microwells, the cultures are treated with microparticles, and changes in the cell index are monitored in real time. Multiple data, including dose response curves, IC50 (a concentration inhibiting 50% cell growth), and cell-specific and particulate-specific cell responses, are obtained from a single set of experiments. SK-MES-1 cells consistently showed more severe effects and lower IC50 values than A549 cells when they were treated with quartz particle suspensions. The different effects detected using the RT-CES technique were related to morphological change and apoptosis, supported by the scanning electronic microscopy and flow cytometry results. The method is further used to test the cytotoxicity of two PM10 standard reference materials of urban air dust and diesel particulates, demonstrating the potential application of this new technique for biomonitoring of air particulates.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...