Revealing the exchange kinetics of thiol-capped Au25 nanoclusters with alkynyl ligands
Abstract
Ligand exchange is an important strategy to functionalize metal nanoclusters (NCs) for enhanced properties. Thiolates and alkynyls have been widely used for NC protection; however, the possibility for alkynyl-for-thiolate exchange as well as the kinetics for the ligand exchange process have remained largely unexplored. Herein, we have reported for the first time a kinetic investigation into the alkynyl-for-thiolate exchange through the reaction of thiolated Au25(SR)18 with the incoming alkynyl ligands. Interestingly, our simulations revealed the electronic and steric effects of alkynyl ligands and the precursor cluster's charge state collectively govern the exchange efficiency and regioselectivity. Notably, the alkynyl-for-thiolate exchange is highly facile when reacting with the nucleophilic lithium or gold(I)–alkynyl complex (Au(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CR) or Li(C
CR) or Li(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CR)), but fails when using HC
CR)), but fails when using HC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CR as the exchange ligand. The Au(C
CR as the exchange ligand. The Au(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh) complex exhibits charge-state-dependent exchange at the S1 or S2 position, whereas the sterically bulky Au(C
CPh) complex exhibits charge-state-dependent exchange at the S1 or S2 position, whereas the sterically bulky Au(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CtBu) complex decelerates the exchange kinetics and universally targets the S1 position as the exchange product. By contrast, the lithium–alkynyl complex (Li(C
CtBu) complex decelerates the exchange kinetics and universally targets the S1 position as the exchange product. By contrast, the lithium–alkynyl complex (Li(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh) or Li(C
CPh) or Li(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CtBu)) preferentially leads to the
CtBu)) preferentially leads to the 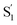 exchange isomer, driven by the ionic Li–C bonding that enhances the C
exchange isomer, driven by the ionic Li–C bonding that enhances the C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C π*-electron density and alkynyl nucleophilicity. Our predictions are further validated by the ligand exchange experiments between phenyl ethanethiol (PET) protected [Au25(PET)18]− and Au(C
C π*-electron density and alkynyl nucleophilicity. Our predictions are further validated by the ligand exchange experiments between phenyl ethanethiol (PET) protected [Au25(PET)18]− and Au(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CtBu). The electrospray ionization mass spectra (ESI-MS) unambiguously confirm the successful substitution of 4, 5 and 6 PET ligands by the –C
CtBu). The electrospray ionization mass spectra (ESI-MS) unambiguously confirm the successful substitution of 4, 5 and 6 PET ligands by the –C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CtBu ligand, and the absorption spectrum drastically changes upon alkynyl exchange. This work establishes an important atomic-level understanding of the alkynyl-for-thiolate exchange mechanism, offering a convenient strategy for realizing alkynyl and thiolate co-protected gold clusters under mild conditions.
CtBu ligand, and the absorption spectrum drastically changes upon alkynyl exchange. This work establishes an important atomic-level understanding of the alkynyl-for-thiolate exchange mechanism, offering a convenient strategy for realizing alkynyl and thiolate co-protected gold clusters under mild conditions.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...