Adsorption of semiflexible wormlike polymers to a bar and their double-chain complex formation
Abstract
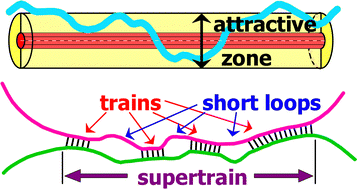
We theoretically study pairing (double-strand complexation) of semiflexible wormlike chains (WLC) due to their side-to-side attraction. Considering binding of two WLCs of high stiffness we start with the case of infinite stiffness of one chain which is replaced with a straight bar. A combination of the quantitative transfer matrix approach with scaling arguments in terms of trains, loops of different sizes, tails and supertrains allowed us to characterize all the regimes of semiflexible chain adsorption on a bar. In particular, we predict a self-similar monomer concentration profile c(r) ∝ r−10/3 near the bar (at distances r below the chain Kuhn length l) at the critical point for adsorption. Such localized critical profile leads to a sharp adsorption transition. Furthermore, we found that supertrains serve as the basic structural elements in WLC complexes leading to bridging, network formation and condensation of semiflexible polymers in dilute solutions. Polymer collapse (precipitation) and redissolution on increasing attraction strength are predicted in qualitative agreement with experiments on aqueous solutions of DNA and F-actin.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...