Plant peptides – redefining an area of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides
Abstract
Covering 1965 to February 2024
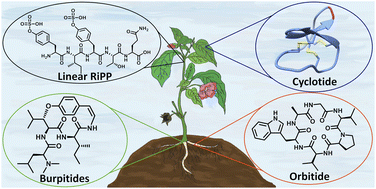
Plants are prolific peptide chemists and are known to make thousands of different peptidic molecules. These peptides vary dramatically in their size, chemistry, and bioactivity. Despite their differences, all plant peptides to date are biosynthesized as ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs). Decades of research in plant RiPP biosynthesis have extended the definition and scope of RiPPs from microbial sources, establishing paradigms and discovering new families of biosynthetic enzymes. The discovery and elucidation of plant peptide pathways is challenging due to repurposing and evolution of housekeeping genes as both precursor peptides and biosynthetic enzymes and due to the low rates of gene clustering in plants. In this review, we highlight the chemistry, biosynthesis, and function of the known RiPP classes from plants and recommend a nomenclature for the recent addition of BURP-domain-derived RiPPs termed burpitides. Burpitides are an emerging family of cyclic plant RiPPs characterized by macrocyclic crosslinks between tyrosine or tryptophan side chains and other amino acid side chains or their peptide backbone that are formed by copper-dependent BURP-domain-containing proteins termed burpitide cyclases. Finally, we review the discovery of plant RiPPs through bioactivity-guided, structure-guided, and gene-guided approaches.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...