Evaluating the impact of phytosynthesized micronutrient nanoparticles on the growth and propagation of mulberry cuttings: dose determination and toxicity concerns†
Abstract
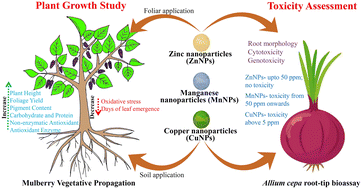
Micronutrient deficiency heavily affects the growth and propagation of mulberry plants. Herein, the present study aimed to determine the optimum dosage of nanoparticle application by investigating the effect of externally applied nano-micronutrients on the growth and biochemical attributes of mulberry cuttings. Among zinc, copper, and manganese nanoparticles applied at 5, 10, and 50 mg kg−1 soil dosages initially through soil admixture and later through foliar spray at rates of 5, 10, and 50 ppm (abbreviated as ZnNP-5, 10, 50; MnNP-5, 10, 50; CuNP-5, 10, 50 respectively), ZnNP-10, MnNP-5, and CuNP-5 were found to be optimum exhibiting better initial root establishment and improved sprouting (71–76%) and survival percentage (88–91%) and, most importantly, quick emergence of leaves (13–14 days) during vegetative propagation. Subsequent investigations substantiated an enhancement in the photosynthetic pigments, protein, and carbohydrate contents, and the antioxidant enzyme reservoir of the cuttings. Moreover, the cytotoxicity and genotoxicity studies carried out through the Allium cepa root tip assay depicted that all the applied dosages of ZnNPs were safe, whereas MnNPs can be used up to the concentration of 10 ppm and CuNPs up to 5 ppm. At the highest applied concentration (50 ppm), ZnNPs, MnNPs, and CuNPs demonstrated 57.42%, 52.51%, and 46.19% mitotic indices having chromosomal aberrations of 3.55%, 6.23% and 7.9%, respectively. Therefore, the evaluation of toxicity concerns addressed the safety issues of the optimized dosage of nanoparticle application in the environment, and this may serve as a reference for future work on the agricultural applications of nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...