Nearly all-active-material cathodes free of nickel and cobalt for Li-ion batteries†
Abstract
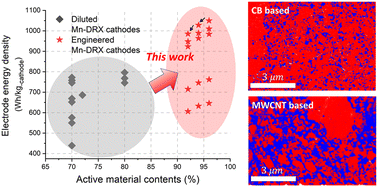
The global transition to electric vehicles and large-scale energy storage systems requires cost-effective and abundant alternatives to commercial Co/Ni-based cathodes (e.g., LiNi0.6Mn0.2Co0.2O2) for Li-ion batteries (LIBs). Manganese-based disordered rock-salts (Mn-DRXs) can outperform conventional cathodes at lower cost, achieving >900 W h kg-AM−1 (per active material, AM), but such performance has been demonstrated exclusively in cell constructions far removed from commercial viability, namely with diluted electrode films (∼70 wt%-AM) containing excessive carbon and binder. Herein, our work involves a comprehensive study to attain AM-concentrated Mn-DRX cathodes (>95 wt%-AM), covering from inherent material properties to the microstructure of electrodes, to address the formidable challenges in Mn-DRX research. We reveal that Mn-DRXs’ failures in AM-concentrated electrodes originate from their extremely low electrical conductivity (10−10–10−8 S cm−1) and the collapse of the electrical network with volume change over cycling. These failure modes are resolved through electrical percolation engineering and enhancement of electrode mechanical properties, allowing our demonstration of nearly all-AM Mn-DRX cathodes (∼96 wt%-AM) and the highest application-level energy density (∼1050 W h kg-cathode−1) reported to date. This work further unveils the trade-off role of Mn-content on Mn-DRXs’ electrical conductivity and volume change, providing guidelines for material design to advance Co/Ni-free LIBs’ technology readiness.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...