Brain-like optoelectronic artificial synapses with ultralow energy consumption based on MXene floating-gates for emotion recognition†
Abstract
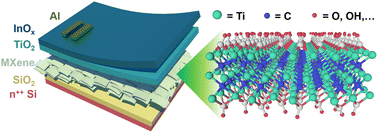
In the new generation of brain-like optoelectronic visual signal processing and artificial perception systems, floating-gate artificial synaptic devices based on two-dimensional materials represent a feasible route. However, the traditional optoelectronic floating-gate artificial synapse is hindered from further development due to complicated processes, such as the need to fabricate additional tunneling layers and photoresponsive layers. Here, an optoelectronic artificial synapse device based on an MXene floating-gate is fabricated. The self-grown TiO2 layer on the ‘111’ surface of MXene is a natural tunneling layer, enhancing the optical response intensity and memory time of postsynaptic currents. The device responds to photoelectric pulses and simulates basic synaptic properties, including excitatory postsynaptic current, paired-pulse facilitation, and short-term/long-term plasticity. In addition, the neural network based on the properties of the device was used to simulate the process of recognizing and classifying objects in the brain after receiving visual signals. Most importantly, as a proof of concept, simulation analyzes the brain wave signals when the brain receives different external stimuli and identifies the subject's mood by classifying the signals. These results indicate that the optoelectronic artificial synapse based on an MXene floating-gate is promising in the application of next-generation brain-like artificial synapse neuromorphic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...