Enhanced activated carbon lithium-ion capacitor electrochemical stability through electrolyte dielectric optimisation†
Abstract
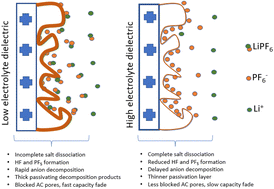
Interactions between electrolyte constituents and active materials strongly influence the capacity, energy density, and cycling stability of energy storage devices. In this study, the role of electrolyte dielectric on the improvement of electrochemical stability is demonstrated using activated carbon (AC) lithium-ion capacitors and symmetric AC/AC cells. 1 M LiPF6 salt is used as the electrolyte and dissolved in different binary solvent mixtures of varying dielectric properties. Floating voltage stability tests show increased floating voltage durations prior to 80% capacity retention as the electrolyte dielectric is increased in half cells and symmetric cells. The increased stability is attributed to improved PF6− anion resistance to oxidation by the enhanced surrounding dielectric and solvation sheath encompassing it at the double layer region of the AC. Post-mortem SEM, nitrogen physisorption and XPS analysis on the extracted electrodes reveal increased deposits of degradation products in the electrolyte with a lower dielectric that reduces the surface area and pores of the AC and causes the faster capacity fade.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Hybrid Ion Capacitors


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...