Highly efficient mRNA delivery with nonlinear microfluidic cell stretching for cellular engineering†
Abstract
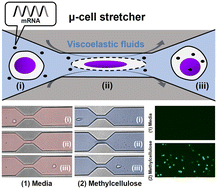
In the past few years, messenger RNA (mRNA) has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent for the treatment and prevention of various diseases. Clinically, mRNA-based drugs have been used for cancer immunotherapy, infectious diseases, and genomic disorders. To maximize the therapeutic efficacy of mRNA, the exact amount of mRNAs must be delivered to the target locations without degradation; however, traditional delivery modalities, such as lipid carriers and electroporation, are suboptimal because of their high cost, cell-type sensitivity, low scalability, transfection/delivery inconsistency, and/or loss of cell functionality. Therefore, new effective and stable delivery methods are required. Accordingly, we present a novel nonlinear microfluidic cell stretching (μ-cell stretcher) platform that leverages viscoelastic fluids, i.e., methylcellulose (MC) solutions, and cell mechanoporation for highly efficient and robust intracellular mRNA delivery. In the proposed platform, cells suspended in MC solutions with mRNAs were injected into a microchannel where they rapidly passed through a single constriction. Owing to the use of viscoelastic MC solutions, a high shear force was applied to the cells, effectively creating transient nanopores. This feature allows mRNAs to be effectively internalized through generated membrane discontinuities. Using this platform, high delivery efficiency (∼97%), high throughput (∼3.5 × 105 cells per min), cell-type-/cargo-size-insensitive delivery, simple operation (single-step), low analyte consumption, low-cost operation (<$1), and nearly clogging-free operation were demonstrated, demonstrating the high potential of the proposed platform for application in mRNA-based cellular engineering research.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Lab on a Chip HOT Articles 2023


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...