8 weeks of 2S-hesperidin prevents a decrease in pO2 at submaximal intensity in amateur cyclists in off-season: randomized controlled trial
Abstract
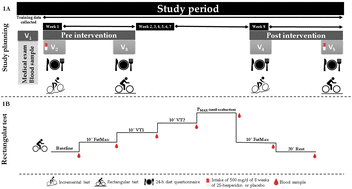
Although chronic supplementation with 2S-hesperidin has been shown to improve performance, to date, the possible mechanisms underlying this effect have not been explored. Therefore, the aim of this study was to assess whether changes in gasometry may be associated with improved performance after the intake of 2S-hesperidin (500 mg d−1, 8 weeks). Forty amateur cyclists (n = 20 2S-hesperidin, n = 20 placebo) performed a rectangular test, during which capillary blood samples were taken at the baseline, FatMax1, ventilatory threshold 1 and 2 (VT1 and VT2), power maximum (PMAX), FatMax2 and excess post-exercise O2 consumption (EPOC) to measure gasometry parameters. Significantly increased CO2 and tCO2 was found at FatMax1, VT1, FatMax2 and EPOC (p = <0.05) after 8 weeks of 2S-hesperidin ingestion. Conversely, the placebo group had a significant decrease in pO2 at VT2 (p = 0.04) during the rectangular test, with no changes in the 2S-hesperidin group. Therefore, chronic supplementation with 2S-hesperidin prevents decreases in pO2 at submaximal intensities in amateur cyclists in an off-season period.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...