Dynamic experiment on remediation of acid mine drainage by iron–carbon microelectrolysis enhancing sulfate-reducing bacteria
Abstract
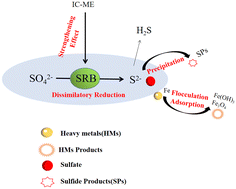
Sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) are easily inhibited by heavy metal ions and low pH when treating acid mine drainage (AMD), so iron–carbon microelectrolysis (IC-ME) was used to enhance SRB activity. The remediation AMD dynamic experiments were carried out by constructing seven groups of IC-ME bioreactors with different mass ratios (4 : 1, 3 : 1, 2 : 1, 1 : 1, 1 : 2, 1 : 3, and 1 : 4 of iron to carbon), and the variation of microbial flora under IC-ME enhancement was explored by high-throughput sequencing. The mechanism of IC-ME was revealed by the variation of ion concentration along the path of the reactor and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray Diffraction (XRD) methods. The results indicated that SRB in the IC-ME bioreactor maintained good biological activity when repairing AMD, with a stable ability of sulfate removal. When the mass ratio of iron to carbon was 3 : 1, the removal efficiency of SO42− was 98.2%, and the removal efficiency of Cu2+, Zn2+, Mn2+, and TFe was all above 99%. SO42− was reduced to S2− by SRB and precipitated with metal ions; Cu2+ was mainly replaced by elemental copper deposited on the iron surface; Zn2+ was mainly removed in the form of sulfide and hydroxide precipitation; Mn2+ was mainly removed by manganese carbonate precipitation and iron ion coprecipitation; TFe was removed by oxide, hydroxide, and flocculation. Microbial community analysis showed that SRB in the IC-ME bioreactor was not a single genus, and its relative abundance and biodiversity were higher than control groups, with higher system stability. This study confirmed that IC-ME enhancing SRB as a low-energy method for AMD remediation will bring extensive application prospects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...