Mechanism of calcium hydroxide-reinforced magnesium-loaded clinoptilolite/phosphoric acid-modified biochar for NH3-N removal from rare earth element tailing wastewater†
Abstract
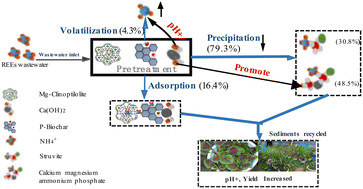
The discharge of rare earth element (REE) tailing wastewater has created serious regional ecological risks. Common biochemical treatments of ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) are inadequate for REE wastewater due to its high ammonia nitrogen, strong acidity, and low C/N ratio. An efficient NH3-N removal material for wastewater treatment was first developed and then recycled as a soil improvement agent for farmland, and the removal mechanism of modified clinoptilolite, biochar, and alkaline substances in combination was investigated. Results show that the composite of MgCl2-modified natural clinoptilolite, biochar modified by phosphoric acid, and Ca(OH)2 had a 7.8 times higher capacity in NH3-N removal than the sum of the individual materials used alone. When calcium hydroxide was replaced by sodium hydroxide, the NH3-N removal efficiency decreased markedly. The higher NH3-N removal efficiency in the calcium hydroxide system could be attributed to the formation of calcium magnesium ammonium phosphate and struvite precipitations. The contribution rate of NH3-N removal mechanisms included volatilization (4.3%), adsorption (16.4%), and precipitation of struvite (30.8%) and calcium magnesium ammonium phosphate (48.5%). The composite, after adsorption saturation, can be recycled in farmland as a potential soil improvement material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...