Capacitive deionization and disinfection of saltwater using nanostructured (Cu–Ag)@C/rGO composite electrodes
Abstract
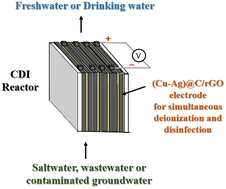
Fresh water shortage is an urgent worldwide problem that needs to be solved. Thus, the main objective of this work was to prepare new nanostructured electrodes for capacitive deionization (CDI) of saltwater with an additional disinfection step to produce fresh water or potential drinking water. Graphene is a two-dimensional carbon with high electrical conductivity and a disinfection ability comparable with nano silver and copper. The (Cu–Ag)@C core–shell nanoparticles were prepared by carbonization of Ag+-β-cyclodextrin-Cu2+ complexes at 673 K for 4 h. The bimetallic Cu–Ag nanoparticles were encapsulated within a carbon-shell, which was dispersed in reduced graphene oxide (rGO) to form (Cu–Ag)@C/rGO composites which acted as the CDI electrode materials. Mainly nano Ag (98–100%) was coated on relatively inexpensive copper in the (Cu–Ag)@C nanoparticles for simultaneous desalination and disinfection. From in situ SAXS, the particle sizes of the (Cu–Ag)@C were in the range of 42–52 nm. More defects and a higher specific capacitance of the (Cu–Ag)@C/rGO composites were observed by Raman spectroscopy and electrochemical analysis (cyclic voltammetry curves (CV)), respectively. The desalination performances associated with the electrosorption efficiencies (21–38%), electrosorption capacities (21–33 mg g−1) and optimized salt removals (504–792 mg g−1 per day) of the composite electrodes in the once-through, four cycles (repeated electrosorption and regeneration under +1.2 and −1.2 V, respectively) CDI processes were greatly improved with a stable recycling performance of 10 h. In addition, the composites have high disinfection efficiencies (79–90%). The unique (Cu–Ag)@C/rGO composite electrodes showed great desalination performances and disinfection efficiencies, and can thus be used for water recycling/reuse, and potentially drinking water, from saltwater, inorganic wastewater and contaminated groundwater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...