Photocatalytic activity towards antibiotic degradation and H2 evolution by development of a Z-scheme heterojunction constructed from 1T/2H-MoS2 nanoflowers embellished on BCN nanosheets†
Abstract
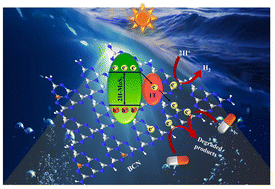
Currently, the design of efficient, cost-effective and sustainable photocatalysts to alleviate the ongoing crisis of ecological contamination is of huge interest. Herein, we have developed an all solid-state Z-scheme-mediated 1T/2H-MoS2@BCN heterojunction via the coupling of 1T/2H-MoS2 with boron-doped g-C3N4 (BCN) using a hydrothermal strategy. In the hybrid structure, the metallic 1T phase serves as a co-catalyst and is an excellent solid state mediator between BCN and the semiconducting 2H phase, thus prolonging the lifetime of the photoinduced charge carriers. Morphological analyses of 1T/2H-MoS2@BCN indicate that the decoration of the BCN nanosheets with 1T/2H-MoS2 nanoflowers and their subsequent close interfacial contact enhances the density of active sites resulting in efficient photocatalytic activity. Owing to the rapid charge separation efficiency of the 1T/2H-MoS2@BCN-10 (10 wt% of 1T/2H-MoS2 to BCN) photocatalyst, it exhibited an optimum photocatalytic hydrogen production of 290 μmol h−1 under visible light irradiation. Moreover, the optimized photocatalyst displayed the highest TCH degradation efficiency (i.e., 95% in 60 min) which is 5.4 and 3.6 fold higher than the individual BCN and 1T/2H-MoS2 components, respectively. Radical trapping experiments and electron paramagnetic resonance analysis confirmed that ˙O2− and ˙OH radicals are the predominant reactive species that result in the accelerated photocatalytic performance. This work opens up a new window towards the development of noble metal-free Z-scheme heterostructures for photocatalytic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...