A laser-induced Fe3O4-graphene nanozyme for catalytic–photothermal synergetic bactericidal applications†
Abstract
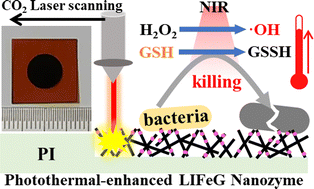
Laser-induced Fe3O4 nanoparticle-modified three-dimensional macroporous graphene is fabricated as a near-infrared light responsive nanozyme via a facile and in situ laser-scanning method under ambient conditions for the first time, showing an excellent catalytic–photothermal synergetic bactericidal ability under a low dose of H2O2 (0.1 mM) and short irradiation time (5.0 min).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...