Sodium hexametaphosphate-treated halloysite based solid-phase extraction of biguanides from dietary supplements†
Abstract
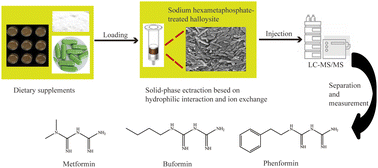
Raw halloysite was purified by using sodium hexametaphosphate and utilized as the solid-phase extraction sorbent for the determination of biguanides from dietary supplements. The purified halloysite was characterized using scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction. The purified halloysite interacted with biguanides through hydrophilic interaction and ion exchange on account of its abundant hydroxyl groups and negative charge. Compared with traditional extraction methods based on hydrophobic interaction and/or ion exchange, the purified halloysite adsorbed more biguanides due to hydrophilicity and ion exchange, with a sample loading volume of up to 100 mL at least. Excellent reproducibility of halloysite purification was achieved, with within-batch (n = 3) and batch-to-batch (n = 3) relative standard deviations in the ranges of 1.5–4.2% and 5.6–8.8%, respectively. Coupled with reversed-phase liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, a low limit of detection of 0.3 μg kg−1 was obtained. The intra- and inter-day mean recoveries of the biguanides spiked at three levels in dietary supplements were within the ranges of 88.5–107.2% and 86.4–102.0%, respectively. The intra- and inter-day precisions were within the ranges of 1.5–6.4% and 5.4–9.9%, respectively. These results indicated that the developed method is efficient for the determination of trace biguanides in dietary supplements.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...