Enhancing the accuracy of mid-infrared spectroscopy-based liver steatosis quantification using digital image analysis as a reference†
Abstract
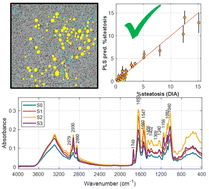
The assessment of liver steatosis is crucial in both hepatology and liver transplantation (LT) surgery. Steatosis can negatively impact the success of LT. Steatosis is a factor for excluding donated organs for LT, but the increasing demand for transplantable organs has led to the use of organs from marginal donors. The current standard for evaluating steatosis is a semi-quantitative grading based on the visual examination of a hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained liver biopsy, but this method is time-consuming, subjective, and lacks reproducibility. Recent research has shown that infrared (IR) spectroscopy could be used as a real-time quantitative tool to assess steatosis during abdominal surgery. However, the development of IR-based methods has been hindered by the lack of appropriate quantitative reference values. In this study, we developed and validated digital image analysis methods for the quantitation of steatosis in H&E-stained liver sections using univariate and multivariate strategies including linear discriminant analysis (LDA), quadratic DA, logistic regression, partial least squares-DA (PLS-DA), and support vector machines. The analysis of 37 tissue samples with varying grades of steatosis demonstrates that digital image analysis provides accurate and reproducible reference values that improve the performance of IR spectroscopic models for steatosis quantification. A PLS model in the 1810–1052 cm−1 region using first derivative ATR-FTIR spectra provided RMSECV = 0.99%. The gained improvement in accuracy critically enhances the applicability of Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) to support an objective graft evaluation at the operation room, which might be especially relevant in cases of marginal liver donors to avoid unnecessary graft explantation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...