Rationally designed far-red emitting styryl chromones and a magnetic nanoconjugate for strip-based ‘on-site’ detection of metabolic markers†
Abstract
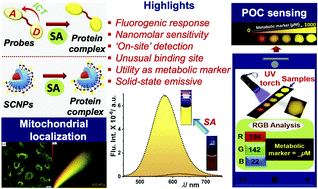
The global burden of liver damage and renal failure necessitates technology-aided evolution towards point-of-care (POC) testing of metabolic markers. Hence in the prevalence of current health conditions, achieving on-site detection and quantifying serum albumin (SA) can contribute significantly to halting the increased mortality and morbidity rate. Herein, we have rationally designed and synthesized far-red emitting, solvatofluorochromic styryl chromone (SC) derivatives SC1 and SC2, and SC2-conjugated fluorescent magnetic nanoparticles (SCNPs) for sensing SA with a fluorogenic response via interacting at an atypical drug binding site. In solution, the highly sensitive and selective fluorogenic response was evaluated by the prominent amplification and blue-shift in the emission maxima of the probes from deep red to dark yellow through an intermediate orange emission. The transformation of the fluorogen into a fluorophore was manifested through spectroscopic measurements. The stabilization of the probes at protein pockets was ascribed to the non-covalent interactions, such as H-bonding, cation-π, and hydrophobic interactions, as unveiled by docking studies. The practical applications revealed the novelty of SC derivatives through (a) the capability to detect SA isolated from real blood samples via a turn-on fluorescence response; (b) the design of a simple, cheap, and portable test-strip using a glass-slide loaded with solid-state emissive SC2, which provided differential emission color of the SC2-HSA complex in solution and the solid-state with increasing concentration of HSA. Moreover, a smartphone-based color analysis application was employed to obtain the ratio of green and red (G/R) channels, which was utilized for quantitative detection of HSA; (c) the biocompatibility of the SC1 was ascertained through confocal laser scanning microscopic imaging (CLSM). Detailed investigation showed that SC1 could entirely localize in the mitochondria and evolve as a promising biomarker for distinguishing cancer cells from normal cells. Additionally, the validation of uncommon binding of SC1 and SC2 between domains I and III was determined using competition experiments with a known site-specific binder and molecular docking studies. This unique property of the probes can be further exploited to understand the cellular intake of HSA-drug complexes in the multifaceted biological system. These results find the utility of SC derivatives as small molecule-based chemosensors for at-home SA detection and as a biomarker for cancer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...