Polythiophene as a near full pH photo-antimicrobial†
Abstract
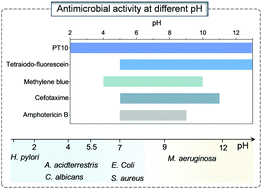
Microbial infections are currently one of the world's major public health concerns, the evolution of which has resulted in the development of multiple tolerances (not just drug or antibiotic resistance), including pH (from extremely acidic to alkaline). Currently various types of antimicrobials have been developed. Although effective, they seldom work in the full pH range due to the existence of acid-/base-reaction sites. Here, we found that polythiophene (PT10), a cationic polymer, was capable of both broad-spectrum photo-antimicrobial activity (Gram positive, Gram negative, Fungal, and cyano-bacteria) and broad pH responsiveness (constant 1O2 generation at pH 2-13). The half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of PT10 for bacteria living in acidic, neutral, and alkaline media were generally lower than 2 μg mL−1 (except M. aeruginosa, pH 12, ∼30 μg mL−1), which were much lower than common antibiotics and other photosensitizers. Besides, the excellent photostability of PT10 allowed long-term light irradiation for antimicrobial performance. In real-world applications, PT10 was explored for the successful in vivo therapy of oral Candidiasis infection under extreme acidic conditions (pH < 3) and the removal of M. aeruginosa at pH 12. Such near full pH, broad-spectrum photo-antimicrobial activity of polythiophene is appealing for extremely acidic or alkaline applications, such as oral infections, vaginitis, and blooms.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry B HOT Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...