PEGylated Prussian blue nanoparticles for modulating polyethyleneimine cytotoxicity and attenuating tumor hypoxia for dual-enhanced photodynamic therapy†
Abstract
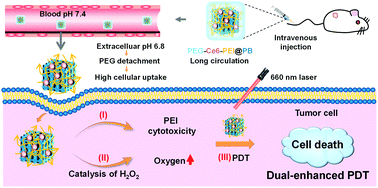
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a promising cancer therapy modality due to its intrinsically negligible side effects and treatment resistance. However, the development of the high-efficiency PDT still remains a challenge. Herein, a nanodrug platform PEG-Ce6-PEI@PB combined tumor acidity-induced polyethyleneimine (PEI) cytotoxicity with an oxygen self-supply property is developed for dual-enhanced PDT. The obtained PEG-Ce6-PEI@PB presents suppressed PEI cytotoxicity and chlorin e6 (Ce6) phototoxicity during the bloodstream before becoming active in tumor tissues/cells. The acidic tumor microenvironment can shed PEG coating to rebound PEI positive charges, facilitating tumor cell uptake and reverting the PEI cytotoxicity to enhance following PDT. Moreover, Prussian blue (PB) nanozymes with catalase-like activity can convert endogenous hydrogen peroxide into oxygen to relieve tumor hypoxia, which is attributed to the photosensitizer Ce6 producing more cytotoxic reactive oxygen species upon laser irradiation to further strengthen PDT. Moreover, PEG-Ce6-PEI@PB exhibits good biocompatibility and long blood circulation. More importantly, PEG-Ce6-PEI@PB-treated breast cancer cells and tumor-bearing mice present effective therapeutic efficacy upon laser irradiation, verifying the synergistic antitumor effects of PEI cytotoxicity and oxygen self-supplying PDT.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...