Doxycycline detection and degradation in aqueous media via simultaneous synthesis of Fe-N@carbon dots and Fe3O4-carbon dot hybrid nanoparticles: a one arrow two hawk approach†
Abstract
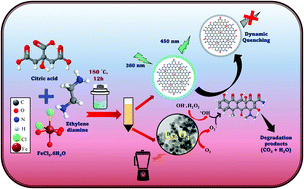
The overuse of antibiotics in recent years presents a huge challenge to society for their removal from the environment. The prolonged presence of antibiotics as environmental pollutants results in the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria faster than new antibiotics to treat diseases they cause. Therefore, a rapid, sensitive, and cost-effective method is urgently required to detect and degrade antibiotics. Given this, a novel strategy has been devised for synthesizing Fe-doped carbon dots (Fe-N@CDs) and iron oxide-carbon dot hybrid nanoparticles (Fe3O4-CDs) in a single step for doxycycline detection and its degradation. For the very first time, the formation of two simultaneous products, i.e., Fe-N@CDs (0 D fluorescent carbon dots) and Fe3O4-CDs (magnetic nanoparticles) in a single step hydrothermal carbonization process by using a sole iron salt (FeCl2) and carbon precursor (citric acid) in the presence of ethylenediamine is reported. The as prepared Fe-N@CDs selectively detect doxycycline with a limit of detection value of 66 ng mL−1 and in the linear range from 0 mg mL−1 to 50 mg mL−1, whereas the other formed products, i.e., Fe3O4-CDs, degrade doxycycline by 70.26% in just 5 min by applying shear force using simply a kitchen blender. The results demonstrated the suitability and application scope in food and environment safety.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Showcasing recent research in materials chemistry from IIT Bombay, IIT Indore and IISc


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...